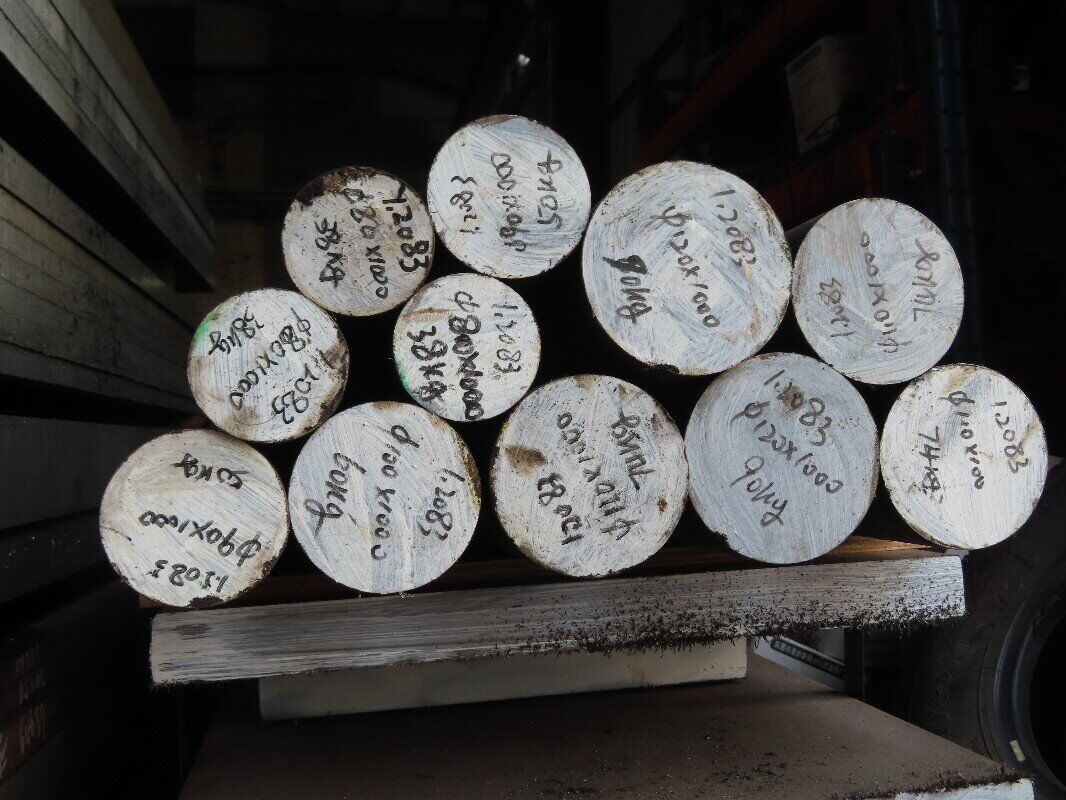
When it comes to high-performance 1.2083 tool steel for demanding applications, 1.2083 tool steel stands out as a preferred choice. Known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high wear resistance, and impressive hardness, this material is widely used in mold-making, plastic processing, and industrial tooling. But what makes 1.2083 tool steel so unique? Let’s dive deep into its properties, applications, advantages, and processing methods to help you understand why it’s a top-tier choice.
What is 1.2083 Tool Steel?
1.2083 tool steel, also known as X42Cr13 or AISI 420, is a high-chromium stainless plastic mold steel. Its primary feature is its high corrosion and wear resistance, making it ideal for use in humid environments or applications that involve corrosive materials. Due to its excellent polishability, it is a top pick for plastic mold and optical component manufacturing.
| Element | Composition (%) |
|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 0.36 – 0.42 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 12.5 – 14.5 |
| Manganese (Mn) | ≤ 1.00 |
| Silicon (Si) | ≤ 1.00 |
| Phosphorus (P) | ≤ 0.030 |
| Sulfur (S) | ≤ 0.030 |
Main Properties of 1.2083 Tool Steel
- High Corrosion Resistance: The high chromium content ensures superior resistance to rust, acids, and moisture exposure.
- Excellent Wear Resistance: Its hardened surface makes it durable under abrasive conditions.
- Good Polishability: Ideal for mirror-finished plastic molds and optical components.
- High Hardness: Can reach 50-52 HRC after proper heat treatment.
- Good Dimensional Stability: Low deformation during heat treatment.
- Decent Machinability: While not the easiest steel to machine, it offers reliable performance when properly processed.
Applications of 1.2083 Tool Steel
- Plastic Mold Manufacturing: Ideal for producing molds that require high polishability and corrosion resistance.
- Medical and Food Processing Equipment: Suitable for environments requiring hygienic and corrosion-resistant materials.
- Cutting Tools and Blades: Used in applications demanding sharp and wear-resistant edges.
- Optical Component Molds: Preferred for lenses and precision plastic parts.
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Machinery: Resistant to aggressive chemicals and cleaning agents.
Heat Treatment Process for 1.2083 Tool Steel
- Annealing: Heat at 780-810°C, then slowly cool to about 600°C before air cooling.
- Hardening: Preheat to 500-600°C, then heat to 980-1030°C and quench in oil or air.
- Tempering: Heat to 200-300°C to adjust hardness and improve toughness.
Advantages of Using 1.2083
- Long Mold Life: Due to its high wear resistance, it extends tool life significantly.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: Corrosion resistance lowers the need for frequent repairs.
- Consistent Performance: Ensures stability and precision over multiple production cycles.
- Great for Harsh Environments: Performs well in humid and chemically aggressive conditions.
1.2083 vs. Other Tool Steels
| Property | 1.2083 | 1.2316 | 1.2311 | 1.2738 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | High | Medium | Low |
| Wear Resistance | High | Medium | Medium | Low |
| Hardness | High | Medium | Medium | Low |
| Polishability | Excellent | Good | Good | Moderate |
| Machinability | Moderate | Good | Excellent | Excellent |
Conclusion
1.2083 is an excellent material for plastic mold applications, industrial cutting tools, and corrosion-resistant environments. With its high hardness, outstanding polishability, and exceptional corrosion resistance, it remains a popular choice among manufacturers worldwide. If you’re looking for a reliable and long-lasting steel, 1.2083 is the way to go.
Interested in purchasing 1.2083 tool steel? Contact us today via email at [email protected] or reach us on WhatsApp at +8613642825398 for the best deals and expert consultation.